Knowing your asset classes – what can you invest in?
Knowing your asset classes – what can you invest in?
In this article, you can learn more about the various asset classes, like equities and bonds, especially their benefits and risks.
If you are familiar with some or all of these asset classes, you can skip to the sections that interest you, or head to our “Why and how you should invest” article.
In this part, we will be covering:
Equities
What are equities?
- Used interchangeably with “stocks” and “shares”, although not exactly the same.
- Equities represent ownership of a publicly traded company which entitles the owner of the stock to a proportion of the corporation's assets and profits equal to how much stock they own.
- Companies issue equity to raise capital in an initial public offering (IPO).
Figure 1: Different types of stocks
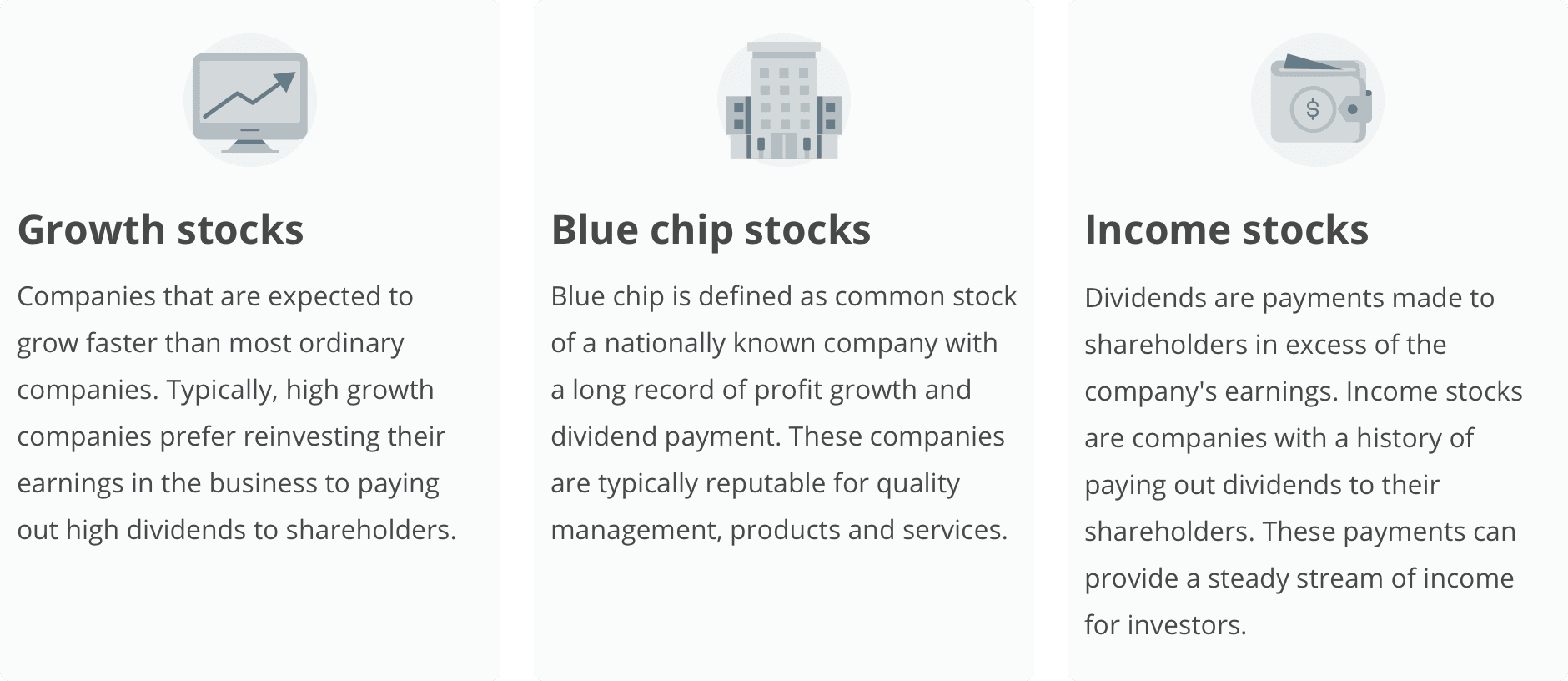
Source: OCBC Wealth Management
Some benefits of investing in equities
- Capital gains/growth: Equities can go up in value based on market movements.
- Earn dividends: The company distributes a portion of its earnings to shareholders.
- Relatively high returns: Potentially higher returns than bonds but also comes with higher risk.
The key risks of investing in equities
- Company-specific: The company may not produce enough revenue or profits and may fail to meet investors’ growth expectations.
- Economic and market uncertainty: Strong companies are not immune to volatility and adverse market news.
- Liquidity: Investors may face difficulty exiting thinly traded equity counters, such as certain small-cap stocks.
Bonds
What are bonds?
- A bond is a loan that the bond purchaser or bondholder makes to the bond issuer (company).
- Like a loan, a bond pays interest periodically (or coupon) and repays the principal (face value) at a stated time, known as maturity.
- Usually interchangeable with, but is a subset of, fixed income.
- Debt issued by governments and corporations to meet their financing needs.
- Investors are paid an interest known as the coupon rate at specific intervals throughout the life of the loan, on top of the principal amount at maturity.
Figure 2: How bonds work
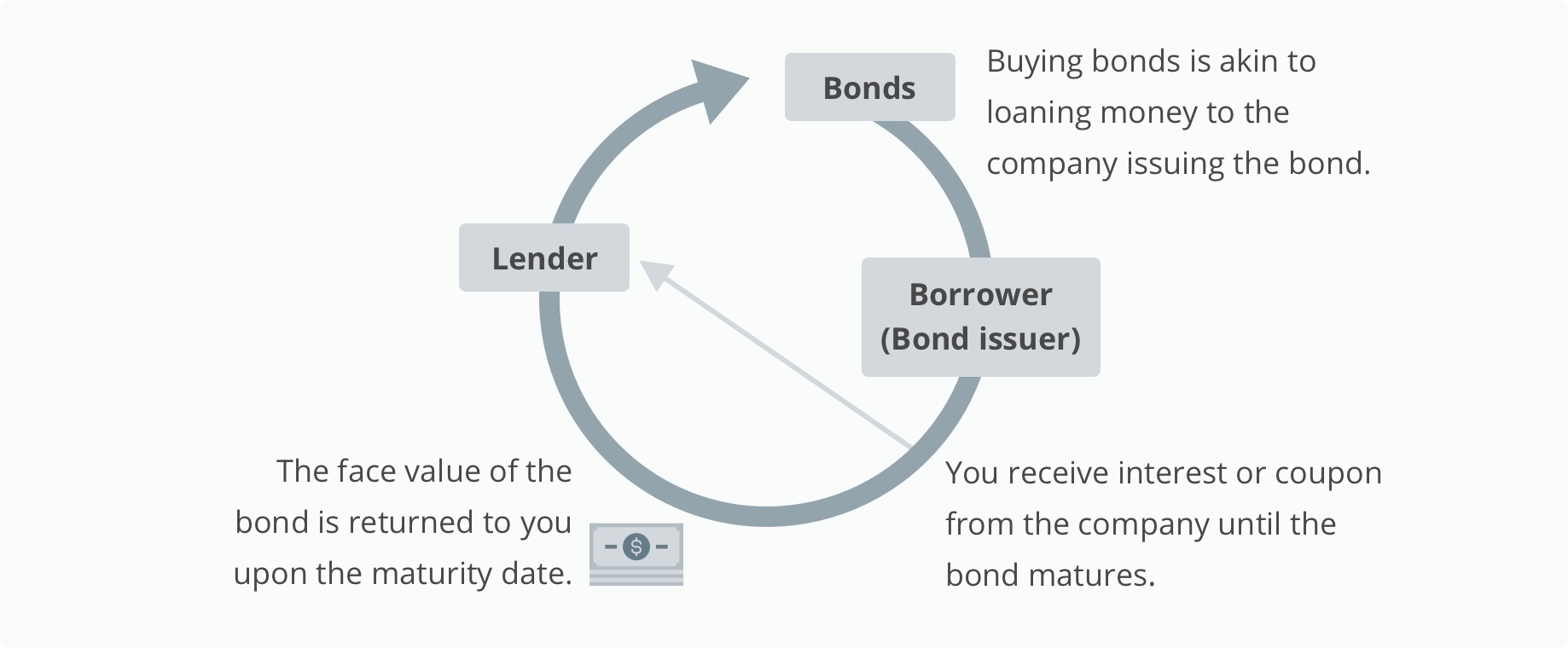
Source: OCBC Wealth Management
Sources of return
- Periodic coupon payments
- Any capital gain (or capital loss) when the bond matures or is called back or sold
- Income from reinvestment of the periodic coupon interest
Some benefits of investing in bonds
- Predictable stream of payments: Provides recurring income and repayment of principal at maturity.
- Lower risk compared to shares: In the event of liquidation, bondholders will get paid before equity shareholders.
- Higher rate of return: More than most saving accounts and fixed deposits of comparable tenure.
The key risks of investing in bonds
- Credit risk: If the issuer goes into default, the future coupon payments and the entire principal may be at risk.
- Interest rate risk: Bond prices and interest rates are negatively correlated; when interest rates rise, bond prices will fall.
- Foreign currency (FX) risk: This exists for bonds that are denominated outside of the customer’s base currency.
Real estate
What are the various types of real estate?
- Residential (e.g. apartments, houses)
- Commercial (e.g. shops, office spaces)
- Industrial (e.g. factories, warehouses)
- Land
Some benefits of investing in real estate
- Recurring income stream: This comes in the form of rent.
- Scarcity: This provides capital appreciation and hedges against high inflation.
- Use of leverage: Allows investors to start with a relatively smaller outlay.
The key risks of investing in real estate
- Liquidity risk: Difficult to sell off within a short period of time without selling below market value or at a loss (with the exception of Real Estate Investment Trusts).
- Vacancy risk: High vacancy rates can lead to negative cash flow if rental income is insufficient to cover the cost of mortgage, maintenance, etc.
- Interest rate risk: Interest rate risk: Real estate investments tend to be financed with loans, thus exposing investors to the risk of higher interest rates.
Commodities
What are commodities?
- Commodities are raw materials used in the production of other goods or services and are typically categorised into hard and soft commodities.
- Hard commodities are natural resources that are mined or extracted from the earth.
- Energy (e.g. crude oil, natural gas)
- Industrial metals (e.g. copper, nickel, iron ore)
- Precious metals (e.g. gold, silver, platinum)
- Soft commodities refer to commodities that are grown and reared.
- Agricultural (e.g. coffee, wheat, rice)
- Livestock (e.g. hogs, chickens)
Some benefits of investing in commodities
- Diversification: Low correlation to stocks and bonds helps to lower portfolio volatility.
- Inflation hedge: Commodity prices typically rise alongside the prices of goods and services due to their limited quantities.
- Potential returns: Growing demand for a commodity can result in its prices rising significantly over time.
The key risks of investing in commodities
- Political risk: Cross-border sanctions may disrupt the supply and/or demand of commodities, causing unexpected price changes.
- Market risk: External factors such as natural phenomena can abruptly alter the prices of commodities, causing your investment to lose value.
- Foreign currency risk: Many commodities are priced in US dollars and thus influenced by the relative strength/weakness of your local currency against the US dollar.
Foreign exchange (FX) investing
What is FX investing?
- The foreign exchange market (FX or forex) is where currencies are traded.
- For multinational companies, this market provides a means of doing business in other countries, facilitating the payment of bills in the local currency.
- For speculators, this market provides opportunities to take advantage of movements in exchange rates.
Some benefits of investing in FX
- Capital appreciation: Profit from the rise in the value of a currency if your view of global market events is correct.
- Hedge against political and event risk: Currencies can be played against each other based on your tactical assessment of important events going on around the world.
- Diversification: Investing in different currencies can diversify your portfolio, particularly if your portfolio is heavily focused on assets denominated in a single currency such as the US dollar.
The key risks of investing in FX
- Volatile: Critical world events can happen in an instant without warning, subjecting currencies to significant short-term volatility.
- Interest rate risk: If a country’s interest rate rises, its currency tends to strengthen; if its interest rate falls, its currency tends to weaken.
- Currency pegs: In many developing countries, exchange rates are fixed to a world leader such as the US dollar. In this circumstance, central banks must sustain adequate reserves to maintain a fixed exchange rate. If there are frequent deficits in payment, the developing country’s currency may face significant devaluation.
Important notices
General disclaimer
This advertisement has not been reviewed by the Monetary Authority of Singapore.
- Any opinions or views of third parties expressed in this document are those of the third parties identified, and do not represent views of Oversea-Chinese Banking Corporation Limited (“OCBC Bank”, “us”, “we” or “our”).
- This information is intended for general circulation and / or discussion purposes only. It does not consider the specific investment objectives, financial situation or needs of any particular person.
- Before you make an investment, please seek advice from your Relationship Manager regarding the suitability of any investment product taking into account your specific investment objectives, financial situation or particular needs.
- If you choose not to do so, you should consider if the investment product is suitable for you, and conduct your own assessments and due diligence on the investment product.
- We are not making an offer, solicit to buy or sell or subscribe for any security or financial instrument, enter into any transaction or participate in any trading or investment strategy with you through this document. Nothing in this document shall be deemed as an offer or solicitation to buy or sell or subscribe for any security or financial instrument or to enter into any transaction or to participate in any particular trading or investment strategy.
- No representation or warranty whatsoever in respect of any information provided herein is given by OCBC Bank and it should not be relied upon as such. OCBC Bank does not undertake an obligation to update the information or to correct any inaccuracy that may become apparent at a later time. All information presented is subject to change without notice.
- OCBC Bank shall not be responsible or liable for any loss or damage whatsoever arising directly or indirectly howsoever in connection with or as a result of any person acting on any information provided herein.
- Investments are subject to investment risks, including the possible loss of the principal amount invested. The information provided herein may contain projections or other forward-looking statements regarding future events or future performance of countries, assets, markets or companies. Actual events or results may differ materially. Past performance figures, predictions or projections are not necessarily indicative of future or likely performance.
- Any reference to a company, financial product or asset class is used for illustrative purposes and does not represent our recommendation in any way.
- The information in and contents of this document may not be reproduced or disseminated in whole or in part without the Bank’s written consent.
- OCBC Bank, its related companies, and their respective directors and/or employees (collectively “Related Persons”) may, or might have in the future, interests in the investment products or the issuers mentioned herein. Such interests include effecting transactions in such investment products, and providing broking, investment banking and other financial services to such issuers. OCBC Bank and its Related Persons may also be related to, and receive fees from, providers of such investment products.
- You must read the Offer Document/Indicative Term Sheet/Product Highlight Sheet before deciding whether or not to purchase the investment product, copies of which may be obtained from your relationship manager.
- Any hyperlink to any third party article, or other website or webpage (including any websites or webpages owned, operated and maintained by third parties) is for informational purposes only and for your convenience only and is not an endorsement or verification of any such article, website or webpage by OCBC Bank and should only be accessed at your own risk. OCBC Bank does not review the contents of any such articles, website or webpage, and shall not be liable to any person for the same.
Global Equities Disclaimer
- Dividend growth is not guaranteed, nor are companies in which you invest obliged to pay dividends;
- Companies may go bankrupt rendering the original investment valueless;
- Equity markets may decline in value;
- Corporate earnings and financial markets may be volatile;
- If there is no recognised market for equities, then these may be difficult to sell and accurate information about their value may be hard to obtain;
- Smaller company investments may be difficult to sell if there is little liquidity in the market for such equities and there may be substantial differences between the buying price and the selling price;
- Equities on overseas markets may involve different risks to equities issued in Singapore;
- With regards to investments in overseas companies, foreign exchange rates may move in an unfavourable direction affecting adversely the valuation of investments in base currency terms.
Foreign Currency Disclaimers
- Foreign currency deposits are subject to inherent exchange rate fluctuation that may provide opportunities and risks. Consequently, exchange rate fluctuations may affect the value of your foreign currency investments or deposits.
- Earning on foreign currency investments or deposits may change depending on the exchange rates prevalent at the time of their maturity if you choose to convert.
- Exchange controls may apply to certain foreign currencies from time to time.
- Any pre-termination costs will be taken and deducted from your deposit directly and without notice.
- Foreign currency deposits, dual currency investments, structured deposits and other investment products are not insured.









